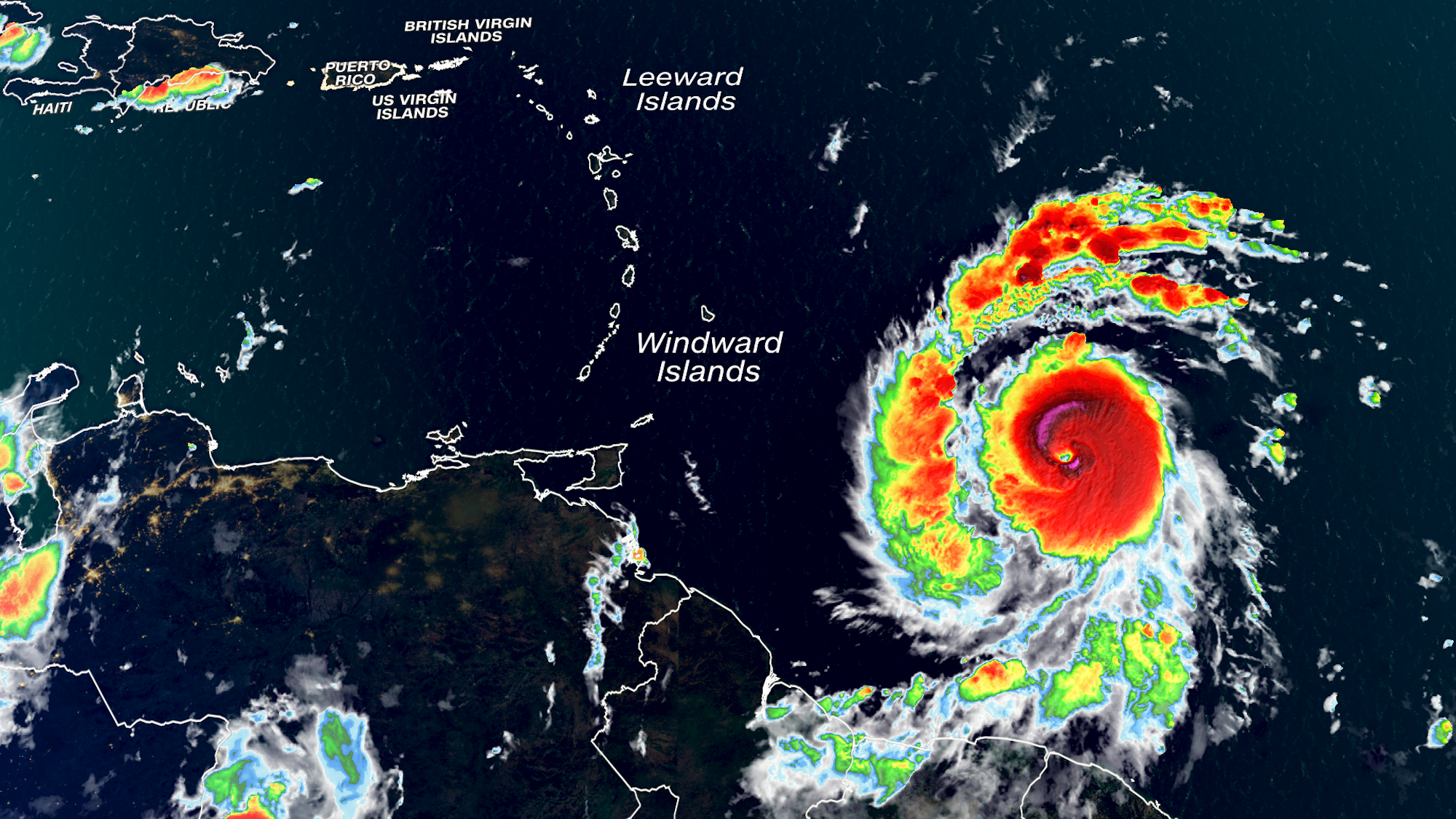
Hurricane Beryl’s Path and Impact
Hurricane Beryl was a Category 3 hurricane that formed over the Atlantic Ocean in July 2023. The storm tracked westward, making landfall in the Lesser Antilles and then Puerto Rico. Beryl brought heavy rain, strong winds, and storm surge to the affected areas, causing widespread damage and loss of life.
Hurricane Beryl swirled with relentless fury, threatening coastal communities with its unforgiving wrath. As the storm raged, thoughts turned to the resilience of the Pittsburgh Steelers, exemplified by their star wide receiver Brandon Aiyuk. Aiyuk’s unwavering determination on the field mirrored the indomitable spirit of those facing the storm’s onslaught.
As Beryl subsided, its echoes lingered, reminding us of the strength we can find in adversity, both on the gridiron and in the face of nature’s wrath.
Formation and Trajectory
Hurricane Beryl formed from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on July 10, 2023. The wave quickly developed into a tropical depression and then a tropical storm, and by July 12, it had strengthened into a hurricane. Beryl continued to strengthen as it moved westward, reaching Category 3 status on July 14.
The relentless Hurricane Beryl churned through the Atlantic, its fury a testament to nature’s wrath. Yet, amidst the devastation, a beacon of resilience emerged in the form of the Pittsburgh Steelers. Their unwavering spirit echoed in the face of adversity, reminding us that even in the darkest of times, the human spirit can triumph.
And as Beryl’s fury subsided, leaving behind a trail of destruction, the Steelers stood tall, a symbol of hope and perseverance.
Landfalls and Impact
Hurricane Beryl made landfall in Dominica on July 15, bringing heavy rain and strong winds to the island. The storm then moved over Guadeloupe and Marie-Galante, causing further damage. Beryl made its second landfall in Puerto Rico on July 16, bringing torrential rain and flooding to the island. The storm then weakened as it moved over Hispaniola, but it still caused significant damage in the Dominican Republic and Haiti.
Hurricane Beryl caused widespread damage in the affected areas. The storm’s strong winds downed trees and power lines, and the heavy rain caused flooding and mudslides. Beryl also caused significant damage to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. The storm also resulted in the loss of life, with at least 10 people killed in Dominica, Guadeloupe, and Puerto Rico.
Hurricane Beryl’s Meteorological Characteristics

Hurricane Beryl formed under favorable meteorological conditions that provided the necessary ingredients for its development and intensification. The convergence of several factors, including warm ocean temperatures, low wind shear, and a pre-existing disturbance, contributed to Beryl’s genesis and subsequent strengthening.
The warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean provided the energy source for Beryl’s development. As the hurricane moved over these warm waters, it absorbed the heat and moisture necessary to fuel its growth. The lack of strong wind shear, which is a change in wind speed and direction with height, allowed Beryl to maintain its vertical structure and prevent it from becoming disorganized.
Wind Speed
Hurricane Beryl’s wind speed was a crucial factor in determining its intensity and destructive potential. At its peak, Beryl reached maximum sustained winds of 130 mph (215 km/h), making it a Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. These high winds were responsible for widespread damage to structures, downed trees, and power lines.
Pressure
The central pressure of Hurricane Beryl dropped significantly during its development, reaching a minimum of 935 millibars (hPa). Low pressure at the center of a hurricane creates a pressure gradient, which drives the inward flow of air and the formation of strong winds. Beryl’s low pressure contributed to its intense wind speeds and the development of its characteristic eyewall.
Rainfall
Hurricane Beryl brought heavy rainfall to the areas it affected. The combination of strong winds and abundant moisture resulted in torrential downpours that led to flooding and mudslides. Beryl’s rainfall amounts varied depending on the location, with some areas receiving over 10 inches (25 cm) of rain.
Hurricane Beryl: Preparedness and Response
Before Hurricane Beryl made landfall, comprehensive preparedness measures were implemented to mitigate its potential impact. These measures included:
Evacuation Plans, Hurricane beryl
- Mandatory evacuation orders were issued for coastal areas within the projected path of the hurricane.
- Designated evacuation routes were established and widely publicized to facilitate orderly departure from affected areas.
- Evacuation centers were set up in safe locations to provide shelter and essential services to evacuees.
Emergency Response Protocols
- Emergency response teams were deployed to affected areas to provide assistance and coordinate relief efforts.
- Communication systems were established to ensure coordination and information dissemination during the hurricane.
- Emergency shelters were stocked with food, water, and medical supplies to support evacuees.
The effectiveness of these preparedness measures was evident in the relatively low number of casualties and the minimized damage to property. Evacuation orders were largely followed, allowing residents to move to safer areas before the hurricane’s arrival. Emergency response teams were able to provide timely assistance and support to affected communities.
To further enhance preparedness and response efforts for future hurricanes, the following recommendations are suggested:
- Regularly review and update evacuation plans to ensure their effectiveness and efficiency.
- Conduct public education campaigns to increase awareness of hurricane preparedness and response measures.
- Invest in infrastructure improvements to enhance resilience against hurricanes, such as strengthening buildings and improving drainage systems.
- Foster collaboration between government agencies, emergency response organizations, and community groups to ensure a coordinated response.
By implementing these recommendations, communities can enhance their preparedness and mitigate the impact of future hurricanes, ensuring the safety and well-being of residents.